When it comes to your skin, keeping an eye on moles isn’t just about aesthetics—it’s about your health. Mole mapping is a simple yet powerful tool that helps track changes in your skin over time. Whether you have a few moles or many, this process can provide peace of mind and, in some cases, early detection of skin cancer.
What Are Moles?
Moles, also known as nevi, are common skin growths that develop when pigment-producing cells, called melanocytes, cluster together. They can appear anywhere on the body and vary in colour, shape, and size. Most moles are brown or black, but some can be flesh-coloured or even slightly reddish. While moles are generally harmless, changes in their appearance can sometimes indicate underlying skin concerns, making regular monitoring an essential part of skincare.
Moles can be present from birth (congenital moles) or develop over time, often increasing in number during childhood and adolescence. Sun exposure can influence the development of new moles and may cause existing ones to darken. Hormonal changes, such as those occurring during pregnancy or puberty, can also affect the size and colour of moles. While most moles remain unchanged throughout life, some may evolve, and any significant alterations should be assessed by a dermatologist.
Although the majority of moles are benign, certain types, such as atypical or dysplastic moles, may have an irregular appearance and a slightly higher risk of developing into melanoma. These moles often have uneven borders, multiple colours, or an asymmetrical shape. Individuals with numerous moles or a family history of skin cancer should pay closer attention to their skin, as early detection of any abnormal changes can significantly reduce health risks.
What Is Mole Mapping?
Mole mapping is a detailed skin examination that involves taking high-resolution images of your moles and other pigmented lesions. These images are then stored and compared over time to identify any subtle changes that may indicate potential skin concerns. Unlike a standard skin check, mole mapping creates a long-term visual record, allowing dermatologists to detect even the slightest variations in size, shape, or colour.
One of the key advantages of mole mapping is its precision. The advanced imaging technology captures high-quality, magnified images of your moles, ensuring even minor changes that might not be visible to the naked eye are documented. This meticulous approach enables dermatologists to assess the overall pattern of moles on your body, distinguishing between harmless natural variations and those that require further investigation. With this systematic tracking, any newly developed or evolving moles can be quickly identified and assessed for potential risk.
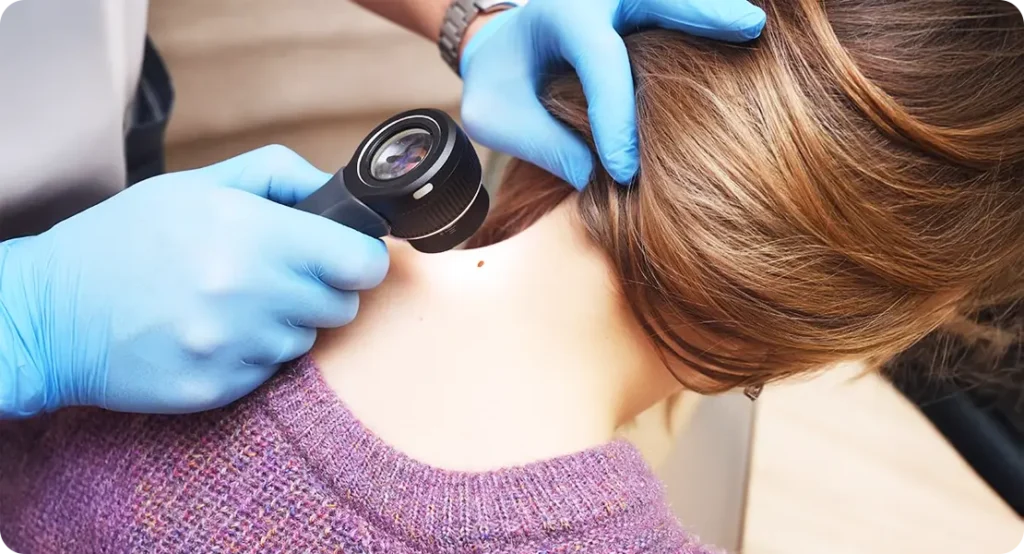
Mole mapping is particularly useful for individuals with numerous moles or a history of abnormal skin growths. Unlike self-checks, which can be inconsistent or prone to human error, professional mole mapping provides an objective, standardised reference point for comparison over time. This means that any changes are not just noticed but accurately measured, reducing unnecessary worry while ensuring that genuine concerns are addressed promptly.
Why Is Mole Mapping Important?
Our skin changes as we age, and so do our moles. While most are harmless, some can develop into skin cancer, including melanoma—the most dangerous form. The challenge is that changes can be gradual and difficult to notice with the naked eye. That’s where mole mapping comes in. It provides a way to spot even the smallest alterations early, making treatment far more effective should an issue arise.
Early detection is crucial when it comes to skin cancer, as treatment options are more successful when conditions are caught in their initial stages. A suspicious mole that may appear normal at first glance can sometimes undergo subtle changes that indicate a developing problem. By comparing images over months or years, dermatologists can detect those subtle transformations that might otherwise go unnoticed, allowing for swift action when necessary. This can make a significant difference in outcomes, particularly in cases where melanoma is detected before it has had a chance to spread.
Beyond cancer detection, mole mapping also provides reassurance to those who have naturally atypical moles but no underlying health risks. Many people worry about their moles simply because they look different, but not all unusual-looking moles are dangerous. Regular mapping and professional assessments ensure that you receive accurate feedback on which moles require monitoring and which are completely harmless. This reduces unnecessary anxiety while keeping your skin health in check with professional oversight.
Understanding Melanoma
Melanoma is the most serious form of skin cancer, developing in the cells that produce pigment (melanocytes). It can spread rapidly if not detected early, making early diagnosis through mole mapping crucial. Unlike other types of skin cancer, melanoma often develops in existing moles or appears as new, abnormal growths on the skin. Recognising the warning signs and knowing your risk factors can help you take proactive steps to protect your health.
One of the key characteristics of melanoma is its ability to change over time. A mole that was once harmless can gradually evolve, showing variations in colour, shape, or size. Unlike common benign moles that remain stable, melanomas often exhibit asymmetry, irregular borders, or uneven pigmentation. They may also become itchy, tender, or start to bleed, which are warning signs that should not be ignored. The challenge is that these changes can be subtle, making regular monitoring essential in detecting early abnormalities before they progress.
Another reason melanoma is particularly dangerous is its potential to spread beyond the skin. If left untreated, cancerous cells can travel to other parts of the body, including the lymph nodes, lungs, liver, and brain. This process, known as metastasis, makes treatment significantly more complex and reduces survival rates. However, when melanoma is identified and treated at an early stage, the likelihood of successful intervention is much higher. This highlights the importance of mole mapping, as it allows dermatologists to track even the most subtle changes in the skin over time, enabling early intervention if necessary.
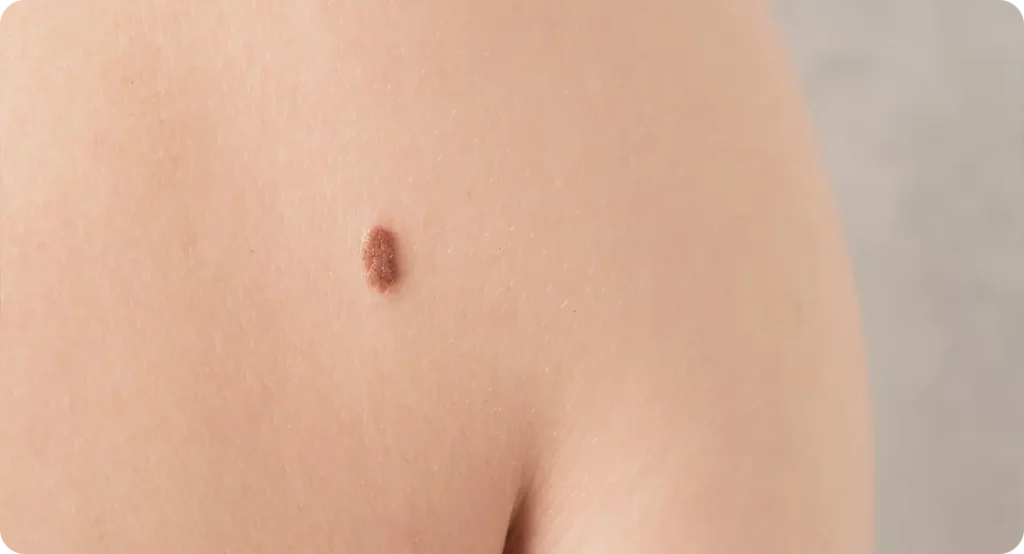
The good news is that melanoma is one of the most preventable forms of cancer when proactive measures are taken. Protecting your skin from excessive UV exposure, regularly checking your moles for changes, and undergoing professional mole mapping are all crucial steps in reducing the risk. For those with higher risk factors, such as a family history of melanoma or a large number of atypical moles, regular monitoring becomes even more important. Through a combination of awareness, early detection, and professional dermatological assessment, the risks associated with melanoma can be significantly minimised.
Who Is at Risk of Melanoma?
While melanoma can affect anyone, certain factors increase the risk of developing it:
- Fair Skin and Light Hair – Individuals with fair skin, light-coloured eyes, and blond or red hair are more susceptible to melanoma due to lower levels of protective melanin in their skin.
- History of Sunburns – If you’ve had frequent or severe sunburns, especially during childhood, your risk of melanoma is higher. UV radiation damages skin cells, increasing the likelihood of abnormal growths over time.
- Excessive Sun Exposure – Spending long hours in the sun, particularly without protection, raises the risk of developing melanoma. This is especially true for those who live in sunny climates or frequently use tanning beds.
- Family History of Melanoma – If a close family member has had melanoma, your risk is significantly increased. This suggests a genetic predisposition to the condition.
- Having Many Moles or Atypical Moles – Those with a large number of moles, or moles with irregular features, are more prone to developing melanoma. Mole mapping is particularly beneficial for tracking these high-risk individuals.
- Weakened Immune System – People with weakened immune systems, due to conditions such as organ transplants or immune-suppressing medications, have an increased risk of developing skin cancers, including melanoma.
How Mole Mapping Helps in Melanoma Detection
Mole mapping plays a vital role in melanoma prevention and early detection. Because melanoma can develop and spread quickly, monitoring changes in moles over time is essential. Through regular imaging and analysis, dermatologists can:
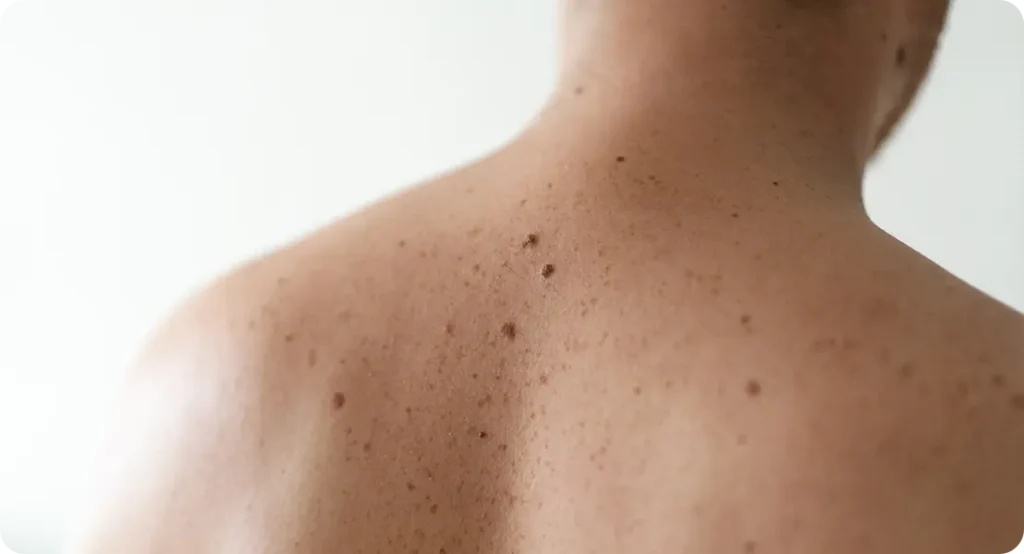
- Identify new or changing moles that could indicate melanoma. New moles or alterations in existing ones can be an early warning sign of melanoma. A mole that increases in size, changes in shape, or develops new colours should be closely monitored. By keeping an accurate record of your skin’s condition through mole mapping, dermatologists can detect these changes early, allowing for timely intervention and reducing the risk of late-stage melanoma.
- Spot subtle changes that may not be visible to the naked eye. Some skin changes are too gradual for an individual to notice without professional imaging. Mole mapping technology enables dermatologists to detect even the smallest variations that may indicate an abnormal growth pattern. These subtle shifts, when identified early, provide an opportunity for treatment before the condition becomes more severe.
- Provide early intervention, significantly improving treatment outcomes. The earlier melanoma is diagnosed, the more successful treatment is likely to be. By identifying concerns at the initial stages, mole mapping enables dermatologists to recommend prompt medical action, whether through biopsy, excision, or other targeted treatments. This proactive approach greatly improves survival rates and minimises the need for more invasive procedures.
- Offer personalised recommendations for skin care and UV protection based on your risk factors. Everyone’s skin is different, and mole mapping allows dermatologists to tailor their advice to your specific needs. If you have a higher risk of developing melanoma due to genetic factors, frequent sun exposure, or fair skin, your dermatologist can recommend personalised sun protection strategies, lifestyle adjustments, and monitoring schedules to keep your skin as healthy as possible.
What Happens During a Mole Mapping Session?
The process is quick, painless, and non-invasive. Here’s what you can expect:
- Initial Assessment – A dermatologist will assess your skin and discuss any concerns you might have. This is an opportunity to highlight any moles you have been worried about and to go over your medical history to determine any risk factors. The consultation helps establish a personalised approach based on your unique skin type and risk profile.
- Imaging – High-resolution photographs of your entire body are taken, with particular focus on your moles and pigmented spots. Advanced imaging technology ensures that even the smallest details are captured, allowing for an accurate baseline that can be referenced in future assessments. This step is essential for detecting gradual changes that might not be noticeable in day-to-day observation.
- Analysis – The images are carefully examined to detect any irregularities. Dermatologists look for patterns in your skin, identifying moles that appear unusual or differ from the rest. If necessary, specific moles may be marked for closer monitoring, and in some cases, further tests such as dermoscopy may be recommended to examine deeper layers of the skin.
- Baseline Record – Your images are securely stored, serving as a reference point for future check-ups. This record enables dermatologists to monitor subtle changes over time and make informed decisions about whether a mole requires further medical attention or can be left alone. A detailed history of your skin’s evolution helps prevent unnecessary procedures while ensuring that any risks are addressed promptly.
- Follow-Up – Regular comparisons help spot any changes over time, ensuring that anything concerning is addressed as early as possible. You may be advised on how often to return for follow-ups based on your skin type and risk factors. Some individuals with a high risk of melanoma may require more frequent monitoring, while others may only need annual check-ups. Dermatologists will also provide guidance on self-monitoring techniques and sun protection strategies to further safeguard your skin health.
Conclusion
Mole mapping is a valuable tool for keeping track of your skin’s health, helping to catch potential issues early and giving you peace of mind. Whether you have a high risk of skin cancer or just want to be proactive, it’s a simple step that can make all the difference.
The London Dermatology Centre specialises in Mole Mapping and can be contacted if you are concerned about any skin changes.
