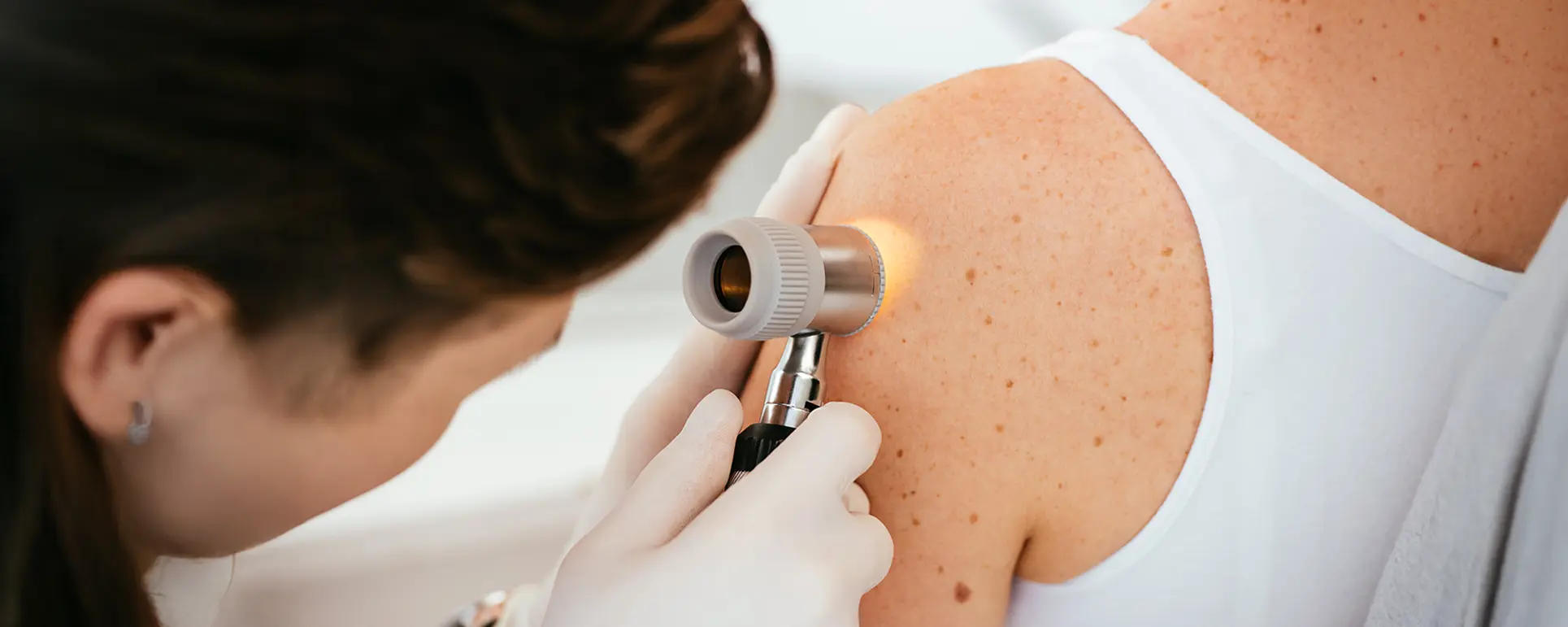
Age spots, also known as liver spots or solar lentigines, are small, dark patches that can appear on areas of your skin that see a lot of sun, like your hands, face, shoulders, and arms. You might notice them becoming more visible as you get older, which can make your skin tone look uneven and sometimes even affect your confidence. These spots are usually harmless, but they often catch your attention because they’re hard to ignore.
Age spots can develop for several reasons, including long-term sun exposure, the natural ageing process, and even genetics. If you’re noticing them on your skin, you’re not alone many people face the same issue and wonder what really works to fade or remove them.
The good news is there are several effective treatments available for you. Depending on your skin type and how noticeable the spots are, you can try topical creams, chemical peels, or even advanced options like laser therapy. Each approach has its benefits, and choosing the right one can make a real difference.
What Causes Age Spots?
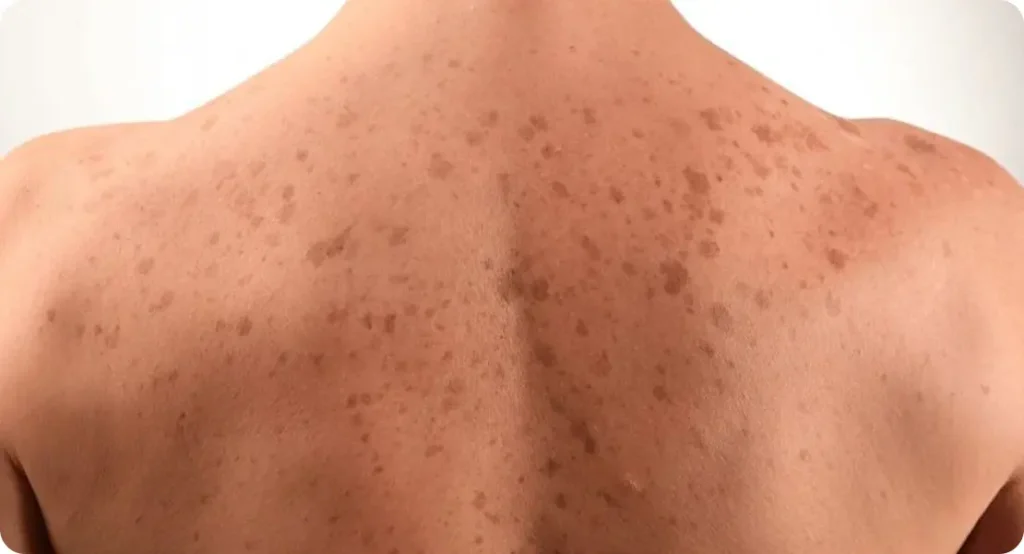
Understanding what leads to age spots is important if you want to find the most effective way to treat them. These darkened patches on the skin usually develop over time due to a combination of factors:
Sun Exposure: One of the most common causes of age spots is prolonged exposure to the sun. Ultraviolet (UV) rays from sunlight trigger the skin to produce more melanin—the pigment that gives your skin its colour. Over time, this excess melanin can accumulate in certain areas, resulting in noticeable dark spots, particularly on the face, hands, shoulders, and arms, which are often exposed to sunlight.
Ageing: As we grow older, our skin naturally undergoes changes. The skin’s ability to regenerate slows down, and the cells that produce pigment may start to cluster unevenly. This means that age spots tend to become more visible as the skin’s natural renewal process becomes less efficient.
Genetics: Sometimes, the tendency to develop age spots runs in families. Your genes can influence how your skin responds to sunlight and how much melanin your body produces, making some people naturally more prone to pigmentation issues than others.
Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, especially those related to pregnancy, menopause, or certain medical conditions, can also trigger changes in skin pigmentation. Women, in particular, may notice age spots or uneven skin tone during periods of hormonal change, as hormones can affect melanin production.
By understanding these causes, you can make better choices for protecting your skin and selecting treatments that address your specific needs. For instance, using broad-spectrum sunscreen, avoiding excessive sun exposure, and consulting a dermatologist for targeted treatments can all help manage and reduce the appearance of age spots.
Topical Treatments for Age Spots
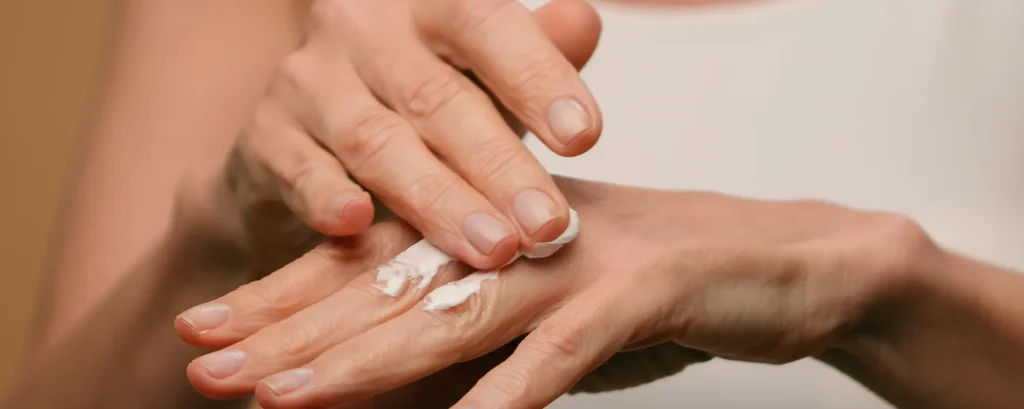

Topical treatments are often the first line of defence for mild pigmentation. These are usually creams or serums that help fade dark spots gradually. While they may not provide instant results, consistent use can significantly improve skin tone over time and prevent new spots from forming.
1. Hydroquinone
Hydroquinone is a skin-lightening agent that works by reducing melanin production in the skin. It is considered one of the most effective topical options for fading age spots, especially when used under the guidance of a dermatologist. Typically, it may take several weeks to show noticeable results, and prolonged use should be monitored to avoid potential side effects such as irritation or sensitivity.
2. Retinoids
Retinoids, such as tretinoin, help increase skin cell turnover, which gradually reduces pigmentation over time. They also improve overall skin texture and stimulate collagen production, giving the skin a healthier, more youthful appearance. While effective, retinoids can sometimes cause mild irritation or dryness initially, so it’s important to start with a lower concentration and build up slowly.
3. Vitamin C
Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant that brightens the skin and inhibits melanin production, making it particularly useful for preventing further pigmentation. In addition to fading age spots, it can help protect the skin against environmental damage from UV rays and pollution. Vitamin C serums are generally well-tolerated and can be layered under moisturisers or sunscreens, making them a versatile addition to any skincare routine.
4. Kojic Acid and Niacinamide
Kojic acid and niacinamide are gentler alternatives to hydroquinone and are suitable for sensitive skin types. These ingredients work slowly to fade dark spots while also improving skin texture and reducing redness or inflammation. Because they are mild, they can be used in combination with other treatments to enhance overall results without causing irritation.
Pros of Topical Treatments: Non-invasive, easy to use, suitable for mild spots, and can be incorporated into a daily skincare routine.
Cons: Results take time, may not work on deeper pigmentation, and some ingredients can cause temporary irritation or dryness.
Chemical Peels for Age Spots
Chemical peels involve applying a solution to the skin that exfoliates the surface layers, removing pigmented cells and encouraging new skin growth. They can be customised depending on the severity of pigmentation and the patient’s skin type, making them a versatile option for treating age spots. Regular treatments, combined with sun protection, can help maintain a more even skin tone over time.
1. Glycolic Acid Peels
Glycolic acid peels are effective for mild to moderate pigmentation. They work by removing the top layer of dead skin cells and stimulating collagen production, which improves both skin tone and texture. These peels are generally well-tolerated and can provide gradual, noticeable improvements without extensive downtime. Multiple sessions may be recommended for optimal results.
2. Trichloroacetic Acid (TCA) Peels
TCA peels are stronger and can treat more stubborn pigmentation that does not respond to gentler treatments. They penetrate deeper into the skin, offering more noticeable results and improving overall skin clarity. Because they are more intensive, they may require professional supervision and careful post-peel care to avoid complications.
3. Jessner’s Peel
Jessner’s peel is a combination of acids designed for patients with sensitive skin. It can effectively target superficial pigmentation while improving overall skin clarity and texture. This peel is often chosen for those who want noticeable results without the higher risk of irritation associated with stronger chemical peels.
Pros: Faster results than creams, can treat larger areas, and can improve overall skin texture.
Cons: Requires downtime, potential for redness or irritation, and may not be suitable for all skin types.
Laser Treatments for Age Spots
Laser therapy is one of the most effective and fastest ways to treat age spots, particularly those that are deeper or more stubborn. Lasers work by targeting melanin in the skin and breaking it down, allowing the body to naturally remove pigmented cells. This treatment is precise, can be tailored to different skin types, and often delivers noticeable results in fewer sessions compared to topical treatments or chemical peels.
1. Q-Switched Laser
Q-switched lasers are specifically designed to target melanin and are ideal for treating stubborn age spots. They deliver energy in short, high-intensity bursts, which break down pigmentation without causing damage to the surrounding tissue. Many patients notice improvements after just a few sessions, although more persistent spots may require additional treatments.
2. Fractional Lasers
Fractional lasers, such as Clear + Brilliant, not only target pigmentation but also stimulate collagen production, improving overall skin texture and tone. They are gentler than ablative lasers, making them suitable for people who want effective results with minimal downtime. Fractional lasers are also useful for improving fine lines and minor scarring, giving the skin a rejuvenated appearance.
3. IPL (Intense Pulsed Light) Therapy
IPL is a light-based treatment that targets both pigment and vascular issues in the skin. It is effective for treating multiple age spots across the face and body and can also help even out overall skin tone. IPL sessions are usually quick, and with proper post-treatment care, patients can often return to their regular routine almost immediately.
Pros: Fast, effective, and can produce visible results in fewer sessions; also helps improve overall skin texture and tone.
Cons: More expensive than topical treatments, may require multiple sessions for best results, and carries a slight risk of side effects such as temporary redness or changes in pigmentation.
Other Treatments
1. Microdermabrasion
Microdermabrasion is a non-invasive procedure that exfoliates the outer layer of the skin, helping to fade superficial age spots over time. It is a mild treatment that is generally suitable for sensitive skin and can improve overall skin texture and brightness. Multiple sessions are often needed to see significant results, and combining it with sunscreen and topical treatments can help maintain the improvements.
2. Cryotherapy
Cryotherapy involves freezing pigmented cells using liquid nitrogen, which causes them to break down and gradually shed. This method is quick and effective, especially for isolated age spots, and can provide noticeable results after a single session. Some patients may experience temporary redness, irritation, or lightening of the treated area, so proper aftercare and sun protection are important.
3. Combination Treatments
Many dermatologists recommend a combination approach to achieve the best results. For example, using topical creams before and after laser or chemical peel treatments can enhance pigmentation reduction and support overall skin health. Combining different treatments can also target both superficial and deeper pigmentation, offering more comprehensive and longer-lasting improvements.
Choosing the Best Treatment
The most suitable treatment for age spots depends on several individual factors:
Severity of Pigmentation: Mild age spots often respond well to topical creams or serums, which gradually lighten the skin over time. Deeper or more stubborn spots, however, may require more intensive treatments such as laser therapy or chemical peels to achieve noticeable results. Understanding the depth of pigmentation can help determine the number and type of sessions needed.
Skin Type: Your skin type plays a key role in treatment selection. Some procedures, like certain chemical peels or lasers, may cause irritation or hyperpigmentation, especially in darker skin tones. Dermatologists can recommend gentler alternatives or adjust treatment settings to minimise risks while still delivering effective results.
Downtime Preferences: Different treatments have varying recovery times. Laser therapy and stronger chemical peels may require a few days of downtime, during which redness or mild peeling is normal. In contrast, topical creams, microdermabrasion, and IPL therapy generally have minimal to no downtime, allowing you to maintain your regular routine.
Budget: Cost is another important consideration. Topical creams are usually the most affordable option, but they require consistent use and patience to see results. Laser treatments and combination therapies tend to be more expensive but can provide faster, more dramatic improvements in fewer sessions.
A consultation with a dermatologist is crucial to determine the best treatment plan for your individual skin needs. They can assess the severity of your pigmentation, consider your skin type and lifestyle, and recommend a tailored approach that maximises results while minimising risks. This personalised guidance ensures both safety and effectiveness in reducing age spots.
Preventing Age Spots
Preventing further age spots is just as important as treating existing ones. By adopting simple daily habits, you can help protect your skin and maintain a more even tone over time.
Sun Protection: Using a broad-spectrum SPF every day is essential to prevent UV-induced pigmentation. Even on cloudy days or when indoors near windows, UV rays can contribute to new age spots. Wearing protective clothing, hats, and sunglasses can provide extra protection and reduce cumulative sun damage.
Healthy Lifestyle: A balanced diet rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals supports overall skin health and helps protect against oxidative stress that can worsen pigmentation. Staying well-hydrated keeps the skin plump and resilient, while avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol can prevent premature ageing and dark spots. Regular exercise also promotes healthy circulation, which benefits skin tone and texture.
Consistent Skincare Routine: Maintaining a daily skincare routine can help keep skin clear and minimise pigmentation. Incorporate products with antioxidants, gentle exfoliants, and moisturisers to support skin renewal and protect against environmental damage. Consistency is key—regular use of these products, combined with sun protection, can significantly reduce the risk of developing new age spots and improve the appearance of existing ones.
By combining protective measures, healthy habits, and a thoughtful skincare routine, you can greatly reduce the likelihood of new age spots forming while enhancing the results of any treatments you choose. Prevention, after all, is often the most effective approach.
Frequently Asked Questions About Age Spots
1. What are age spots?
Age spots, also known as liver spots or sunspots, are flat, darkened patches of skin that appear due to excess melanin production. They most commonly develop on areas of the body that are regularly exposed to the sun, such as the face, hands, shoulders, and arms. Although they are harmless and do not pose a health risk, age spots can affect a person’s appearance and confidence.
2. What causes age spots?
Age spots develop primarily due to prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays, which stimulate melanin production in the skin. As we age, our skin becomes less efficient at regenerating, making pigmentation more noticeable. Genetics can also play a role, as some people are naturally more prone to developing dark spots. Additionally, hormonal changes, particularly in women during menopause or pregnancy, can trigger pigmentation.
3. Are age spots dangerous?
Generally, age spots are harmless and do not require medical treatment. However, it is important to monitor any spots that change in size, shape, or colour, as these could be signs of skin cancer. Consulting a dermatologist for any unusual or rapidly changing spots ensures early detection of potential issues.
4. Can age spots go away on their own?
Mild age spots may fade slightly over time, but most do not disappear completely without intervention. Sun protection is essential to prevent existing spots from darkening and to reduce the formation of new ones. Without proper care, age spots tend to persist and may become more noticeable as skin ages.
5. What are the most effective treatments for age spots?
The choice of treatment depends on the severity of pigmentation and skin type. Topical creams containing ingredients like hydroquinone, retinoids, vitamin C, kojic acid, or niacinamide can gradually fade mild spots. Chemical peels, such as glycolic acid, TCA, or Jessner’s peel, exfoliate the skin and remove pigmented cells for faster results. Laser treatments, including Q-switched lasers, fractional lasers, and IPL therapy, are highly effective for deeper pigmentation and often show visible improvement after a few sessions. Other options, such as microdermabrasion or cryotherapy, may be used alone or in combination with other treatments to enhance results.
6. How long do treatments take to work?
The timeframe for results varies depending on the method used. Topical creams usually require several weeks to a few months of consistent use before noticeable improvement occurs. Chemical peels may show results within one to three weeks, depending on the strength of the solution. Laser treatments often require one to three sessions, with improvements visible after one or two weeks. Using a combination of treatments can sometimes speed up results and provide longer-lasting outcomes.
7. Are age spot treatments painful?
Most treatments for age spots are well tolerated. Topical creams and serums are completely painless, while chemical peels may cause mild stinging or temporary redness. Laser treatments can feel like a warm or snapping sensation on the skin, but discomfort is usually minimal. Your dermatologist can recommend numbing creams or cooling techniques to make the procedure more comfortable if needed.
8. Can age spots come back after treatment?
Yes, age spots can recur, especially if skin is continually exposed to sunlight without protection. Maintaining daily sun protection and following up with maintenance treatments can help prevent spots from returning. Adopting a consistent skincare routine and avoiding tanning beds also reduces the likelihood of recurrence.
9. Are some treatments better for darker skin?
Darker skin types are more prone to irritation or post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation from certain treatments. Gentler options, such as niacinamide, mild chemical peels, and fractional lasers, are usually safer and more effective for these skin tones. A dermatologist can personalise treatment plans to ensure safety and optimise results for all skin types.
10. How can I prevent age spots in the future?
Preventing age spots involves consistent sun protection and healthy skincare habits. Daily application of a broad-spectrum SPF 30 or higher helps shield the skin from UVA and UVB rays. Wearing protective clothing, such as hats and long sleeves, further reduces sun exposure. Incorporating antioxidants, moisturisers, and gentle exfoliation into your skincare routine supports skin health, while avoiding tanning beds prevents artificial UV damage that can trigger pigmentation.
Final Thought: Finding the Best Treatment for Your Age Spots
Choosing the right approach for age spots can feel overwhelming given the many options available. While topical creams are ideal for mild pigmentation, chemical peels and laser treatments often provide faster, more noticeable results for stubborn spots. Combining treatments under the guidance of a dermatologist can maximise effectiveness and maintain healthy, glowing skin. You can get in touch with us to book a consultation and discuss the most suitable age spots treatment at the London Dermatology Centre.
References:
1. Fabian, I.M., 2023. Topical Hydroquinone for Hyperpigmentation: A Narrative Review. Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology, 16(4), pp. 23-29. Available at: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10723018
2. Mukherjee, S., 2006. Retinoids in the treatment of skin aging. Journal of Cutaneous and Aesthetic Surgery, 9(4), pp. 1-6. Available at: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2699641/
3. Correia, G., 2023. Efficacy of topical vitamin C in melasma and photoaging. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology, 22(1), pp. 1-6. Available at: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/jocd.15748
4. Negishi, K., Akita, H., Matsunaga, Y. et al. (2018) Prospective study of removing solar lentigines in Asians using a novel dual-wavelength and dual-pulse width picosecond Nd:YAG laser, Lasers in Surgery and Medicine, 50(8), Available at: https://doi.org/10.1002/lsm.22820
5. Kauvar, A., Lee, C., Goldberg, D. et al. (2022) Treatment of facial and non-facial lentigines with a 730 nm picosecond titanium:sapphire laser is safe and effective, Lasers in Surgery and Medicine, 54, pp. Available at: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/lsm.23450