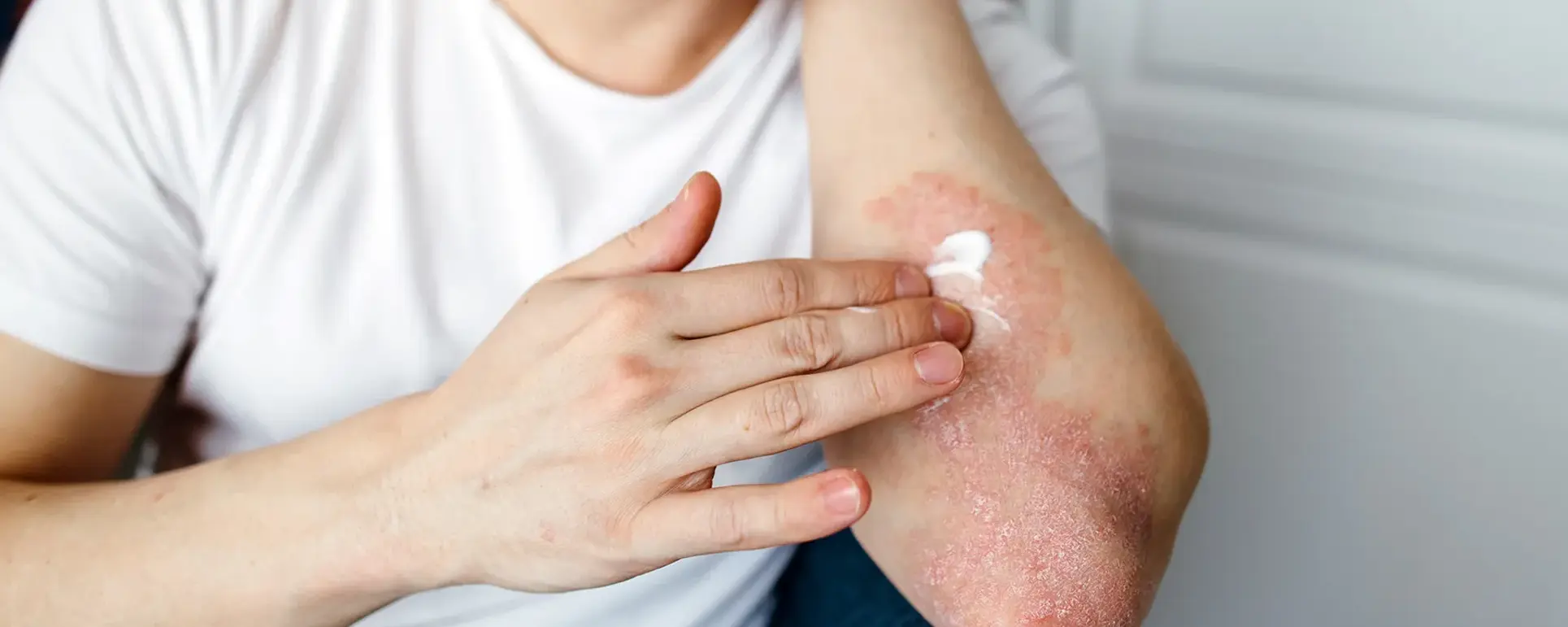
Psoriasis is more than just a skin condition it’s a chronic autoimmune disorder that can feel frustrating and confusing if you’re living with it. Essentially, what happens is that your skin cells start multiplying much faster than they should, leading to those red, scaly, and often itchy patches that can appear on different parts of your body. If you’ve ever looked in the mirror and wondered why your skin is reacting this way, you’re not alone. Millions of people around the world deal with psoriasis, yet the exact reasons behind it can still feel like a mystery.
If you’ve been diagnosed with psoriasis, or even if you’re just curious about what might trigger it, understanding the root causes can be really helpful. When you know what’s happening beneath the surface, it can give you a sense of control and guide the steps you might take to manage your symptoms.
In this article, I’ll take you through the main factors that contribute to psoriasis, from genetic predispositions to an overactive immune system, as well as environmental and lifestyle triggers that might make your symptoms worse. By the end, you’ll have a clearer picture of why psoriasis develops and some ideas for how you might approach it, whether through lifestyle adjustments, treatments, or simply understanding your body better.
Psoriasis doesn’t just affect your skin it can also impact your confidence, daily comfort, and even your emotional well-being. You might notice flare-ups at the most inconvenient times, or feel self-conscious about visible patches when you’re out in public. Understanding what triggers these flare-ups can make a big difference in how you manage the condition day to day. By learning more about the root causes, you can start to identify patterns in your own experience, whether it’s stress, weather changes, diet, or other environmental factors that seem to make your symptoms worse.
The Role of Genetics in Psoriasis

One of the major factors behind psoriasis is genetics. If someone in your family has psoriasis, it means you might be at a higher risk of developing it yourself. Studies have identified specific genes that influence how your immune system functions and how quickly your skin cells regenerate. These genetic factors can make your skin more prone to the rapid cell turnover that leads to the red, scaly patches you see in psoriasis.
Psoriasis is considered a genetically linked condition. This means that inheriting certain genes from your parents can increase your susceptibility. However, it’s important to understand that genetics alone usually aren’t enough to trigger the condition. Most people who carry these genes won’t develop psoriasis unless other factors, such as immune system overactivity, stress, or environmental triggers, also play a role.
Understanding the genetic aspect can help you see why psoriasis sometimes seems to “run in families.” If you’ve noticed relatives with psoriasis, it doesn’t mean you’re destined to have it, but it does indicate that you may need to be more aware of early signs and potential triggers.
Knowing your genetic risk can empower you. It gives you a chance to take preventive steps, work closely with your dermatologist, and manage your skin more proactively. Genetics sets the stage, but it’s only one part of the story your lifestyle, environment, and immune system all play important roles in whether psoriasis develops and how severe it might become.
Immune System Overactivity: The Main Culprit
At the heart of psoriasis lies an overactive immune system. Normally, your immune system is your body’s protector, defending you against harmful invaders like bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens. But in psoriasis, your immune system starts behaving differently it becomes overactive and mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells.
This overactivity leads to an increased production of T-cells, which are a type of white blood cell that usually defends your body against infections. In people with psoriasis, these T-cells misidentify healthy skin cells as threats. When that happens, they trigger a rapid cycle of skin cell production. You might notice it as red, inflamed patches covered with silvery scales the hallmark of psoriasis.
The consequences of this immune system malfunction go beyond just visible skin changes. This overactivity is central to why psoriasis can flare up unexpectedly and why it often becomes a chronic, long-term condition. You may experience cycles of improvement and worsening, which can be frustrating and affect your daily life.
Several factors can worsen this immune overactivity. For example, stress, infections, certain medications, or even injury to the skin can act as triggers, causing your immune system to “overreact” and worsen your symptoms. By understanding these triggers, you can start to notice patterns in your own experience and take steps to manage flare-ups more effectively.
Understanding that psoriasis is driven by your immune system can help you make sense of why treatments often focus on calming immune responses rather than just addressing the surface symptoms. By targeting the underlying immune dysfunction, you can better manage flare-ups and work toward longer periods of clearer, healthier skin.
Environmental Triggers: The Catalyst for Psoriasis Flares
While genetics and immune system overactivity set the stage for psoriasis, environmental triggers often act as the sparks that ignite flare-ups. These triggers can vary widely from person to person, and what affects you might not affect someone else. By understanding these factors, you can start to identify patterns and take proactive steps to manage your condition.
Stress: Emotional or physical stress is one of the most common triggers. When you’re stressed, your body releases chemicals that can activate your immune system, increasing the likelihood that it will attack healthy skin cells. Many people notice flare-ups during particularly stressful periods, so learning stress management techniques like meditation, exercise, or deep breathing can be really helpful.
Infections: Certain infections, especially strep throat, can trigger psoriasis in susceptible individuals. For example, Guttate psoriasis, which appears as small, drop-like lesions on the skin, often develops after a strep infection. If you’re prone to this type of psoriasis, being vigilant about infections and seeking prompt treatment can help reduce flare-ups.
Skin injuries: Cuts, burns, or even sunburns can provoke psoriasis in a phenomenon known as the Koebner response. Essentially, psoriasis lesions can appear at the site of skin trauma. This is why protecting your skin from injury and practicing gentle skincare is especially important if you have psoriasis.
Medications: Some medications, such as lithium (used for mood disorders), beta-blockers, and certain anti-malarial drugs, can worsen psoriasis in some individuals. If you notice new flare-ups after starting a medication, it’s worth discussing alternatives with your doctor.
Weather: Weather can also play a role. Cold, dry conditions can strip your skin of moisture and trigger flare-ups, while hot, humid conditions may worsen symptoms for some people. Adjusting your skincare routine with moisturizers and protective measures can help you maintain healthier skin throughout the seasons.
Understanding these environmental triggers is crucial for managing psoriasis effectively. By observing your own patterns and avoiding known triggers wherever possible, you can reduce the frequency and intensity of flare-ups and feel more in control of your skin’s health.
The Connection Between Psoriasis and Other Health Conditions
Psoriasis doesn’t just affect your skin it’s a systemic condition that can have an impact on your whole body. If you have psoriasis, it’s important to understand that it may put you at a higher risk for other health issues. Being aware of these connections can help you take proactive steps to protect your overall health.
Psoriatic arthritis: Some people with psoriasis develop a type of arthritis called psoriatic arthritis. If you notice joint pain, swelling, or stiffness along with your skin symptoms, it could be a sign of this condition. Early detection and treatment can make a big difference in preventing joint damage and maintaining your mobility.
Cardiovascular disease: Research shows that psoriasis is linked to an increased risk of heart disease. Chronic inflammation associated with psoriasis may affect your blood vessels and heart health over time. This means that managing your skin condition isn’t just about appearance it’s also about protecting your heart.
Diabetes: The inflammation and immune system dysfunction seen in psoriasis may also raise your risk of developing diabetes. If you have psoriasis, it’s worth monitoring your blood sugar levels and discussing your risk factors with your healthcare provider.
Depression and anxiety: Living with a visible, chronic condition like psoriasis can affect your mental health. The discomfort, flare-ups, and impact on your appearance can contribute to stress, anxiety, or depression. If you notice changes in your mood or mental wellbeing, it’s important to reach out for support whether that’s through a therapist, support group, or your healthcare provider.
Being aware of these related conditions can help you take a more holistic approach to your health. Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider are essential not only for monitoring your psoriasis but also for keeping an eye on potential comorbidities. By staying proactive, you can manage your skin symptoms while also protecting your overall health and wellbeing.
The Role of Diet and Lifestyle in Managing Psoriasis
While genetics and an overactive immune system are major contributors to psoriasis, the choices you make in your daily life can also play an important role in managing the condition. Paying attention to your diet, staying active, managing stress, and avoiding certain habits can all help reduce flare-ups and improve your overall health.
Anti-inflammatory diet: What you eat can have a direct impact on inflammation in your body, which is closely linked to psoriasis. Including foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, like salmon and mackerel, along with plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, can help calm inflammation. Healthy fats from avocados, olive oil, and nuts are also beneficial. By focusing on an anti-inflammatory diet, you’re not just supporting your skin you’re supporting your overall wellbeing.
Weight management: Maintaining a healthy weight is another key factor. Excess weight can put more pressure on your joints and may worsen psoriasis symptoms, especially in areas like your elbows, knees, and lower back. Even small lifestyle changes, like incorporating regular exercise or making healthier food choices, can make a noticeable difference in your skin and overall energy levels.
Stress management: Stress is a major trigger for psoriasis flare-ups. When you feel overwhelmed or anxious, your immune system can overreact, which may worsen your symptoms. Practising relaxation techniques, such as yoga, meditation, or even just deep breathing exercises, can help you manage stress more effectively. Taking time for yourself isn’t just good for your mind it’s good for your skin too.
Avoid smoking and alcohol: Habits like smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can aggravate psoriasis. Cutting back or eliminating these habits entirely can help reduce flare-ups and improve your overall health. Even small changes in these areas can have a meaningful impact on both your skin and your general wellbeing.
By paying attention to your diet and lifestyle, you can give yourself more control over your psoriasis. While these strategies may not replace medical treatments, they can complement them, helping you manage symptoms, reduce flare-ups, and feel healthier in your day-to-day life.
FAQs about Psoriasis:
1. What exactly causes psoriasis?
Psoriasis is primarily caused by a combination of genetics, an overactive immune system, and environmental triggers. If you have a family history of psoriasis, your chances of developing it are higher. Your immune system can mistakenly attack healthy skin cells, causing them to grow too quickly. Factors like stress, infections, skin injuries, certain medications, and even weather changes can trigger flare-ups. So, while genetics set the stage, other elements often act as the sparks that bring psoriasis to the surface.
2. Can psoriasis be cured?
Currently, there’s no permanent cure for psoriasis, but the good news is that it can be managed effectively. Treatments ranging from topical creams and phototherapy to systemic medications can help reduce flare-ups and improve your skin’s appearance. Lifestyle changes, such as diet, exercise, stress management, and avoiding triggers, can also make a big difference. With the right approach, you can keep psoriasis under control and maintain a good quality of life.
3. How do I know if my psoriasis is mild, moderate, or severe?
The severity of psoriasis is usually assessed based on the extent of your skin involvement, the location of plaques, and the impact on your daily life. Mild psoriasis generally covers a small area, while moderate psoriasis affects larger areas or visible parts like your hands and face. Severe psoriasis involves widespread plaques, significant discomfort, or impacts your mental wellbeing. Your dermatologist can help determine the severity and recommend the most suitable treatment plan for you.
4. Can stress really make psoriasis worse?
Yes, stress is a well-known trigger for psoriasis flare-ups. When you’re stressed, your body releases chemicals that can overactivate your immune system, which may cause new plaques to appear or worsen existing ones. Managing stress through techniques like meditation, deep breathing, yoga, or even hobbies you enjoy can help reduce flare-ups and improve your overall wellbeing.
5. Are there foods that can help or worsen psoriasis?
Certain foods can influence inflammation in your body, which is linked to psoriasis. Eating an anti-inflammatory diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and omega-3 fatty acids from fish like salmon can help reduce flare-ups. On the other hand, processed foods, excessive sugar, and saturated fats may worsen symptoms for some people. Keeping a food diary can help you identify personal triggers and discover what works best for your skin.
6. Can psoriasis affect other parts of my health?
Yes, psoriasis is more than just a skin condition. It’s associated with several other health issues, including psoriatic arthritis, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and mental health challenges like depression or anxiety. Being aware of these connections is important, as it allows you to take a holistic approach to your health. Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider can help monitor both your skin and overall wellbeing.
7. What can I do to prevent flare-ups?
While you may not be able to prevent psoriasis entirely, you can reduce the frequency and severity of flare-ups by taking proactive steps. This includes avoiding known triggers, maintaining a healthy diet and weight, managing stress, protecting your skin from injury, and following your dermatologist’s treatment plan. Keeping a symptom diary can also help you notice patterns and identify what specifically triggers your psoriasis.
8. Is psoriasis contagious?
No, psoriasis isn’t contagious at all. You can’t catch it from touching someone who has it, sharing towels, or being close to them. It’s an immune system condition, not an infection, so you don’t need to worry about passing it on or picking it up from anyone else.
9. Does psoriasis always stay the same over time?
Not necessarily. Psoriasis can change in how often it flares up and how severe it feels. Some people experience long periods of clear skin, while others have cycles of flare-ups and remission. Factors like stress, weather, or even new medications can cause changes, so staying aware of triggers is key.
10. Can lifestyle changes really make a difference?
Yes, they absolutely can. While lifestyle adjustments won’t cure psoriasis, they can help manage symptoms and reduce flare-ups. Eating an anti-inflammatory diet, staying active, keeping your skin moisturised, avoiding smoking and heavy drinking, and managing stress can all make your skin healthier and your flare-ups less frequent.
Final Thoughts: Managing Psoriasis and Your Well-Being
Psoriasis is a complex condition with multiple causes, including genetic factors, immune system dysfunction, and environmental triggers. While there is no cure for psoriasis, understanding its root causes is the first step in managing it effectively.
At the London Dermatology Centre, we offer specialised care for individuals dealing with psoriasis. If you’re struggling with psoriasis and want to explore the best treatment options, our team is here to help. You can visit our Psoriasis Clinic in London to book a consultation and find a personalised treatment plan that works for you.
References:
1. Harden, J. L. (2015). The Immunogenetics of Psoriasis: A Comprehensive Review. Journal of Investigative Dermatology, 135(5), 1163–1170. DOI:10.1038/jid.2014.492. Available at: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0896841115300111
2. Liu, S., 2024. Triggers for the Onset and Recurrence of Psoriasis: A Review. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) – Molecular Basis of Disease, 1868(1), p. 166389. Available at: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10860266/
3. Sun, L., 2014. The Immunological and Genetic Aspects in Psoriasis. CORE. Available at: https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/81870303
4. Puig, L., 2017. Cardiometabolic Comorbidities in Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 6(12), p. 118. Available at: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5796008/
5. Chen, H., 2012. Psoriasis Patients Are Enriched for Genetic Variants That Contribute to Anti-Viral Immunity. PLOS ONE, 7(7), e40035. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0040035